Search a node in Binary tree
Search a node in a Binary tree using recursion or iterative solution. For example, a binary tree contains elements- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7. Here, if 7 is searched then return true but if 9 is searched then return false because it is not available in the binary tree.
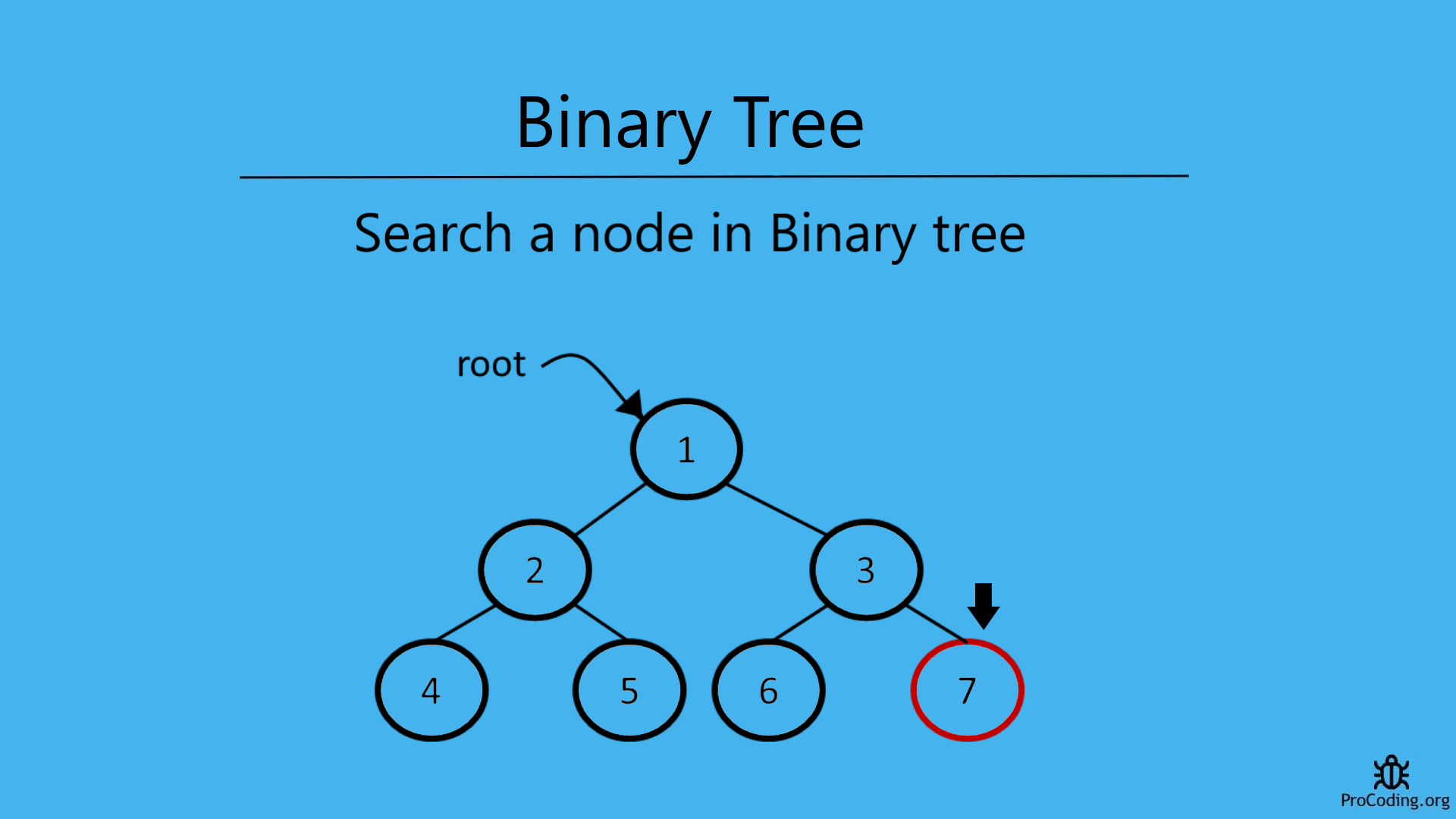
In a Binary Tree, to search a node we have to traverse each node and check if that node is available in the tree.
We can solve this problem in two ways-
Recursive solution
For recursive solution we have to check each node one by one recursively as we have done in binary tree recursive traversal and if required node is found then return True otherwise return False.
Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.data = data
self.right = None
def search_node(root, num):
if root is None:
return False
if root.data == num:
return True
val = search_node(root.left, num)
if val:
return True
return search_node(root.right, num)
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
print(search_node(root, 7))
JavaScript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.data = data;
this.right = null;
}
}
function searchNode(root, num) {
if (!root) return false;
if (root.data === num) return true;
let val = searchNode(root.left, num);
if (val) return true;
return searchNode(root.right, num);
}
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
console.log(searchNode(root, 7));
Output
True
Iterative solution
For iterative solution, we have to traverse each node in level order and if required node is found then return True otherwise return False.
Python
import queue
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.data = data
self.right = None
def search_node(root, num):
if root is None:
return False
q = queue.Queue()
q.put(root)
while not q.empty():
node = q.get()
if node.data == num:
return True
if node.left:
q.put(node.left)
if node.right:
q.put(node.right)
return False
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
print(search_node(root, 7))
JavaScript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.data = data;
this.right = null;
}
}
function searchNode(root, num) {
if (!root) return false;
const q = [];
q.push(root);
while (q.length > 0) {
let node = q.shift();
if (node.data === num) return true;
if (node.left) q.push(node.left);
if (node.right) q.push(node.right);
}
return false;
}
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
console.log(searchNode(root, 7));
Output
True
Time complexity: The time complexity of both of these solution will be O(n) because we are just traversing each element of node one by one.