One-to-One Relationship in Database
One-to-one relationships in the database are important when organising data so that each record in a table can relate to just one record in another table.
One-to-one relationships in the database are important when organising data so that each record in a table can relate to just one record in another table.
In database design, a one-to-one (1:1) relationship is a type of relationship between two entities where each instance of one entity is associated with a single instance of another entity, and vice versa. This relationship type is less common compared to many-to-one or many-to-many relationships, but it is vital in scenarios where information about an entity needs to be separated for organizational, security, or practical reasons.
One-to-One Relationship
A one-to-one relationship exists when a row in Table A is linked to exactly one row in Table B, and a row in Table B is linked to exactly one row in Table A. The relationship is often established to store optional or sensitive information or to logically separate different types of data related to a single entity.
ER Diagram
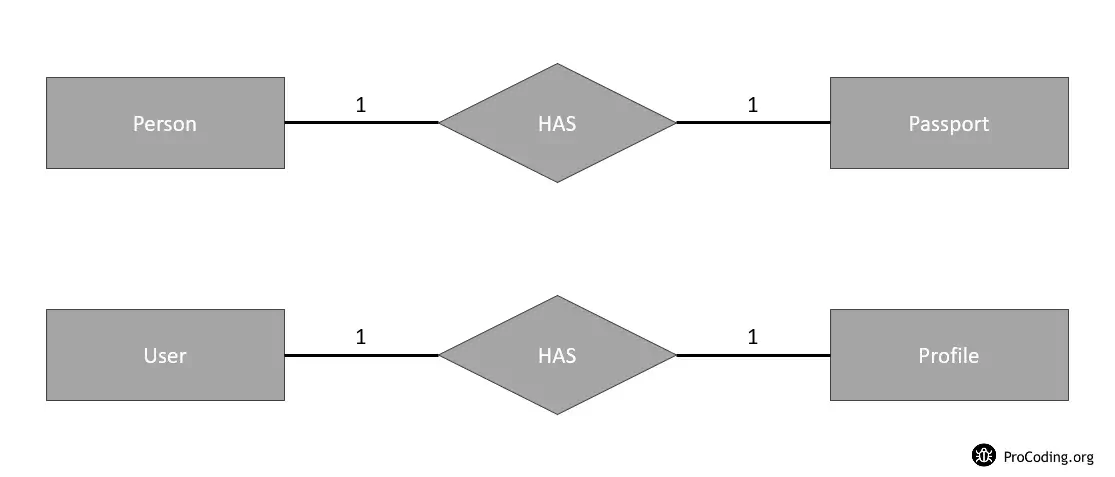
If we create the tables based on the ER diagram then we will have three tables like this -
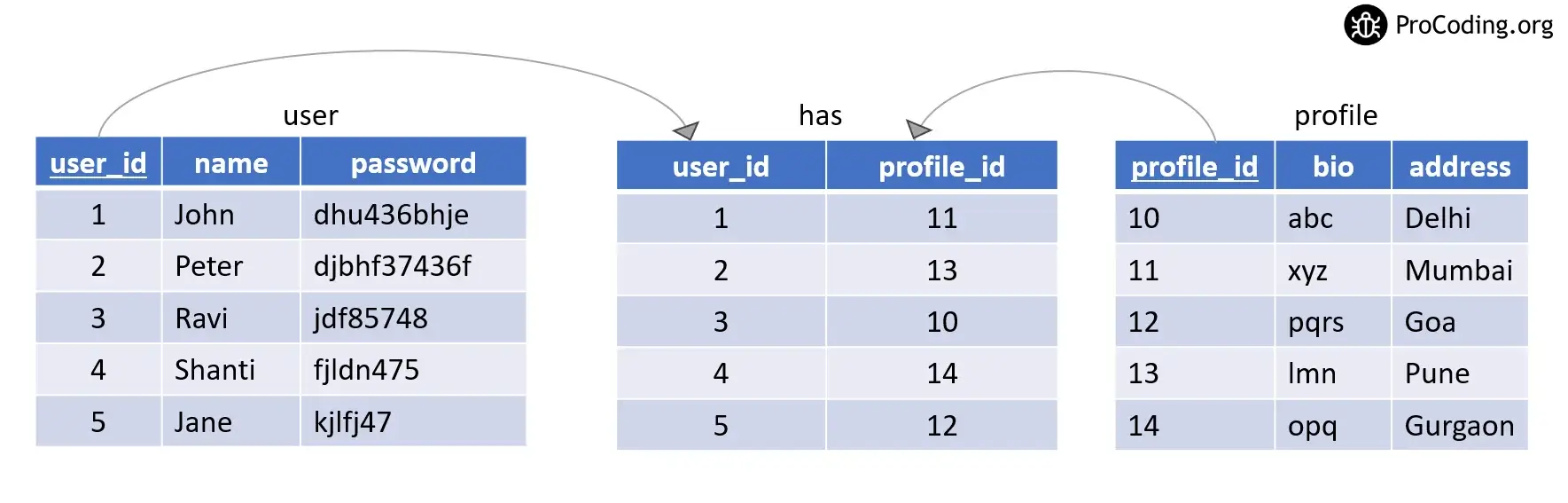
Here, we can simply drop the intermediate table and store the reference of the user table into the profile table as FOREIGN KEY.
Updated tables will be -

So far things look the same as the One-To-Many relationship but we have to keep one thing in mind a user ID can only be assigned to one profile at a time.
SQL Query
Now let's see the query to generate such tables -
CREATE TABLE User (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
password VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE Profile (
profile_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
bio VARCHAR(255),
address VARCHAR(512),
user_id INT UNIQUE,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES User(user_id)
);
Here, notice that we are marking user_id as UNIQUE which will ensure that only a unique entry will exist for a User i.e., a user will only have only one profile.
Similarly, if we create such tables for the user and passport then a user will only have one passport.