Introduction to Arrays
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The array is used to store multiple data of the same type together.
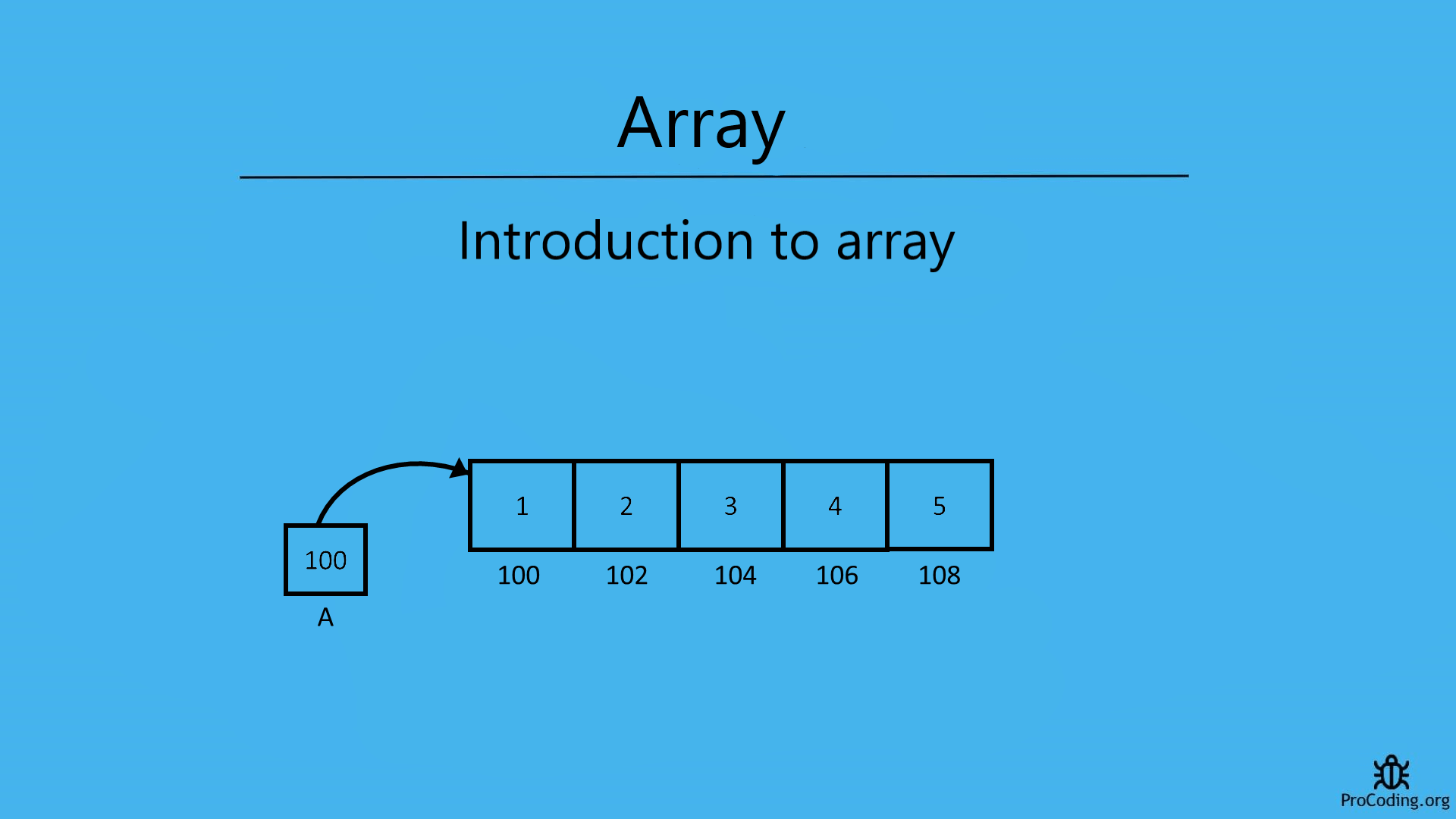
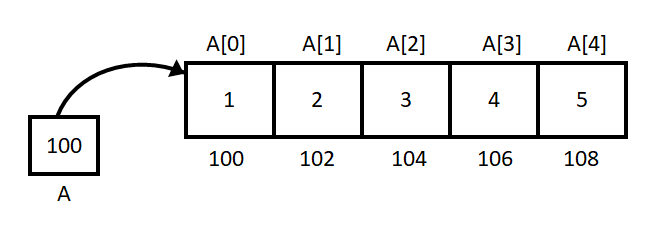
Array is a linear data structure. The elements are stored at contiguous memory locations in an array.
An array contains elements of homogeneous data type or similar data type and size of array is fixed i.e, it cannot be increased or decreased once declared.
But there is an exception, in some languages like Python, JavaScript etc. elements of different data type can be stored and size can be modified. But this rule of similar data type and fixed size of the array holds strictly for languages like C, C++ and Java etc.
Terminologies
- Element: Each item in an array is known as elements.
- Index: Each memory location in array is uniquely identified by its index.
Types of indexing in an array
In most of the programming language index of the array starts from 0 that's why it is known as zero-based indexing. But some languages follow different conventions for indexing of an array.
- zero-based indexing (0): The first element of the array starts at index 0.
Languages: C, C++, Python, Java, JavaScript etc. - one-based indexing (1): he first element of the array starts at index 1.
Languages: ALGOL 68, AWK, COBOL, Julia, Lua, MATLAB etc. - n-based indexing (n): The base index of an array can be chosen. For some programming languages allowing n-based indexing also allow negative index values, and other scalar data types like enumerations, or characters may be used as an array index.
Languages: Ada
Representation of Array
An array is represented in various ways in different languages. Following are the main things used to declare an array.
- Data type: Data type of the element to be stored in an array.
• Not required for weakely typed languages like Python, JavaScript PHP etc. - Name: Name of an array is used to indentify it and access its elements.
• Required for all the languages. - Size: Length of an array i.e., number of elements to stored in an array.
• Not required for weakely typed languages like Python, JavaScript PHP etc.
Python
# var_name = []
arr1 = [] # empty array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # array with elements
C
// data_type var_name[size];
int arr1[5]; // empty array
int arr2[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} // array with elements
C++
// data_type var_name[size];
int arr1[5]; // empty array
int arr2[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} // array with elements
JavaScript
// let var_name = []
let arr1 = [] // empty array
let arr2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] // array with elements
Array operations
- Traversal: Traverse all the array elements one after another.
- Insertion: Add an element at the given position. another.
- Deletion: Delete an element at the given position.
- Searching: Search an element using the given index or by value.
- Updating: Update an element at the given index.
- Sorting: Arrange elements in the array in a specific order (incresing or decreasing).
- Merging: To merge two arrays into one.