Stack using array
In this tutorial, we will implement a stack using array by using the fixed array and dynamic array method with their time and space complexity. Basically the size of the array in case fixed array implementation is always fixed but in case of dynamic array implementation size of the array may grow if stack overflow occurs.
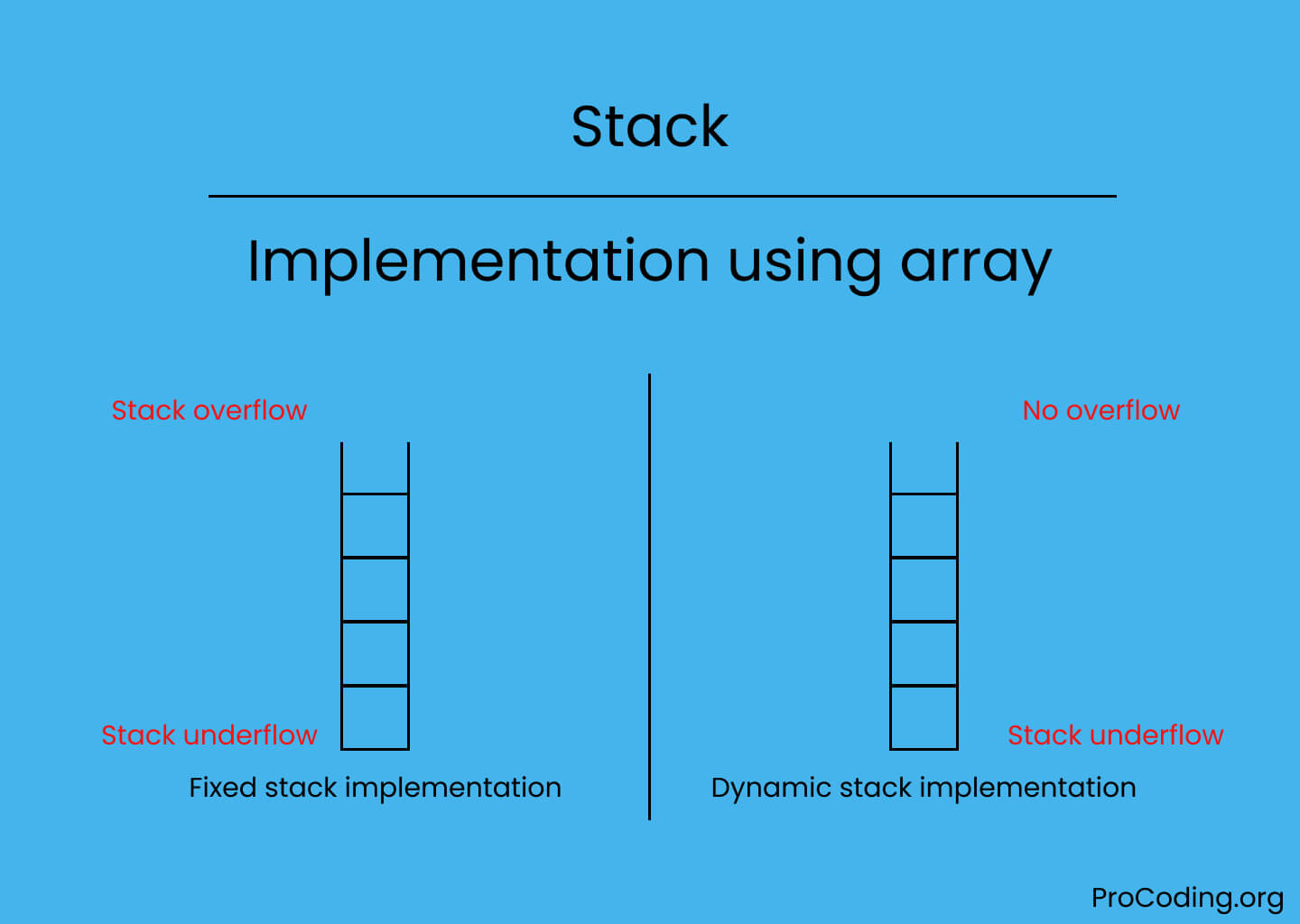
Stack is a linear data structure which works in LIFO (Last In First Out) or FILO (First In Last Out) order. In this tutorial we will implement stack using an array.
Four main operations on stack:
- Push: Adds new item on the top of stack.
- Pop: Removes an item from the top of stack.
- Peek: Returns top element of stack.
- is_empty: Check if stack is empty or not.
Implementation of stack using array
There are two ways to implement stack using arrays i.e.,
Fixed array implementation
In case of fixed array implementation of stack, the size of array is always fixed that's why when we try to push an element on stack if already the stack is full then Stack overflow exception will be raised and if we try to pop an element if stack is already empty then Stack underflow exception will be raised.
Python
class Stack:
def __init__(self, size=10):
self._stack = []
self._size = size
def is_empty(self):
return len(self._stack) <= 0
def push(self, data):
if len(self._stack) >= self._size:
raise Exception('Stack overflow')
else:
self._stack.append(data)
def pop(self):
if len(self._stack) <= 0:
raise Exception('Stack underflow')
else:
return self._stack.pop()
def peek(self):
if len(self._stack) <= 0:
raise Exception('Stack underflow')
else:
return self._stack[-1]
def length(self):
return len(self._stack)
stack = Stack(5)
stack.push(5)
stack.push(2)
stack.push(3)
stack.push(9)
stack.push(6)
print(stack.peek())
print(stack.pop())
print(stack.length())
print(stack.peek())
JavaScript
class Stack {
#stack;
#size;
constructor(size = 10) {
this.#stack = [];
this.#size = size;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.#stack.length <= 0;
}
push(data) {
if (this.#stack.length >= this.#size)
throw "Stack overflow";
else
this.#stack.push(data);
}
pop() {
if (this.#stack.length <= 0)
throw "Stack underflow";
else
return this.#stack.pop();
}
peek() {
if (this.#stack.length <= 0)
throw "Stack underflow";
else
return this.#stack[this.#stack.length - 1];
}
length() {
return this.#stack.length;
}
}
const stack = new Stack(5);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(9);
stack.push(6);
console.log(stack.peek());
console.log(stack.pop());
console.log(stack.length());
console.log(stack.peek());
Output
6
6
4
9
| Operation | Time complexity |
|---|---|
| Space complexity (for n push) | O(n) |
| Time complexity of push() | O(1) |
| Time complexity of pop() | O(1) |
| Time complexity of length() | O(1) |
| Time complexity of is_empty() | O(1) |
Dynamic array implementation
In case of dynamic array implementation of stack, the size of array is growable i.e., whenever stack reaches at the condition of overflow then the size of array will be increased that's why Stack overflow exception will never raise but Stack underflow may raise in case of stack is empty.
Python
class Stack:
def __init__(self, size=10):
self._stack = []
self._size = size
def is_empty(self):
return len(self._size) <= 0
def push(self, data):
if len(self._stack) >= self._size:
self._resize()
self._stack.append(data)
def pop(self):
if len(self._stack) <= 0:
raise Exception('Stack underflow')
else:
return self._stack.pop()
def peek(self):
if len(self._stack) <= 0:
raise Exception('Stack underflow')
else:
return self._stack[-1]
def length(self):
return len(self._size)
def _resize(self):
new_stack = [*self._stack]
self._size = 2 * self._size
self._stack = new_stack
stack = Stack(2)
stack.push(5)
stack.push(4)
stack.push(3)
stack.push(9)
print(stack.peek())
print(stack.pop())
print(stack.peek())
JavaScript
class Stack {
#stack;
#size;
constructor(size = 10) {
this.#stack = [];
this.#size = size;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.#stack.length <= 0;
}
push(data) {
if (this.#stack.length >= this.#size)
this.resize();
this.#stack.push(data);
}
pop() {
if (this.#stack.length <= 0)
throw "Stack underflow";
else
return this.#stack.pop();
}
peek() {
if (this.#stack.length <= 0)
throw "Stack underflow";
else
return this.#stack[this.#stack.length - 1];
}
length() {
return this.#stack.length;
}
resize() {
const newStack = [...this.#stack];
this.#size = 2 * this.#size;
this.#stack = newStack;
}
}
const stack = new Stack(2)
stack.push(5)
stack.push(4)
stack.push(3)
stack.push(9)
console.log(stack.peek())
console.log(stack.pop())
console.log(stack.peek())
Output
9
9
3
| Operation | Time complexity |
|---|---|
| Space complexity (for n push) | O(n) |
| Time complexity of push() | O(1) |
| Time complexity of pop() | O(1) |
| Time complexity of length() | O(1) |
| Time complexity of is_empty() | O(1) |
Advantages of implementing stack using array
- Easy to implement.
- Operations require less time.
Disadvantage of implementing stack using array
- Space may be occupied but not used if the size of stack is small.